Virtual Optics Laboratory
Computational Electromagnetics
曾雪峰教授以及其研究團隊研究概況:
由於非結晶體(例如:生物體)的光學性質極度複雜、牽涉到大量的變數,傳統上研究巨觀隨機介質的光學性質常用近似解(例如:Diffusion Approximation, Monte Carlo method, etc.),然而此種近似解的精確度和可信度有待商榷。應用新的演算法(Pseudospectral time-domain method),使用電腦平行計算的技術,如今這個問題已經可以由數值方法解Maxwell’s equations 而得到精確解。本團隊利用數值方法解馬克士威方程式,建構虛擬光學實驗,在一個無雜訊的模擬實境中,精確計算光的散射現象,幫助分析光學性質。
一個很重要的應用是在於精確地分析生物組織的光學性質。生醫光電是現代科技發展的重點之一,然而欲發展光學篩檢癌症的技術,必須先對正常以及病變的生物組織的光學性質有精確的瞭解,才能針對其光學性質相異之處進行分析和篩檢。利用新的演算法研究方法以平行電腦做模擬,本研究計畫將致力於分析巨觀隨機介質生物組織(包括生物組織)的光學性質,進而幫助促進生醫光電新技術的研發。
另外,還有幾個研究方向,包括: Photonic Nanojet, Monte Carlo simulation,二維光子晶體聚光現象,負折射率透鏡(Negative Refractive index super lens)、以及軟性顯示器之導光模擬分析等等,都是我們正在進行,或即將進行的研究。
歡迎加入研究團隊:
招生條件:
勤奮、肯努力。
若有程式設計基礎經驗者更好。
實驗室設備:
實驗室的主要設備為個人電腦。目前的大型設備就屬一台32個計算核心的平行電腦,它可以讓運算更為快速,及算更龐大的光散射問題。
Fig.1 Multiprocessor cluster

I.
Research Group Introduction
隨著時代的進步,電腦速度的提升,讓我們得以利用電腦來分析許多電磁問題,而本實驗室研究專注在數值電磁模擬與分析,使用的程式語言為Matlab、C/ C++、Fortran,至於使用的方法主要為時域有限差分法FDTD (finite-difference time-domain method)。我們希望可以利用模擬的技術,在製程實作前可以預知結果,以便節省不必要的金錢浪費與時間。另一方面也希望模擬生物醫學方面的電磁問題,畢竟醫療和我們息息相關,如果我們可以瞭解細胞對光的特性或其他種種資訊,相信不管是對診斷或是醫療方面都將大有幫助,最後也期待利用此技術將未來診斷所需時間大幅減少,到便利商店幾分鐘就可以拿到報告,這對人類將是一大福音。
II.
2006~2007 Research Projects
(1) NANOJET
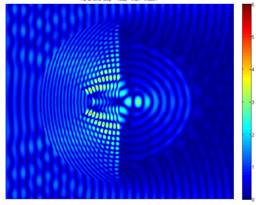
Light scattering through a semi-cylinder in 2D is modeled using finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method. Illuminated by a plane wave, the localized nanojets are generated at the shadow-side surface of the semi-cylinders. The nanojets have waists smaller than the diffraction limit and propagate over several optical wavelengths without significant diffraction.
Fig.2 light scattering by a semi-cylinder of n = 2.2
(2)
Using

(3) SURFACE PLASMON
The local field enhancement and surface plasmon resonance of metallic nanoparticles were used to focus and to manipulate light. We investigated the local field enhancement of symmetric silver nano-cylinder pairs by using finite-difference time-domain method. The intensity of local field enhancement is found to depend on separation distance, radius ratio, and numbers of nano-cylinder.
Fig.3 The magnetic field for a single Ag cylinder of radius r = 25nm with the incident resonance wavelength of 344 nm.
(4)
PHOTONIC
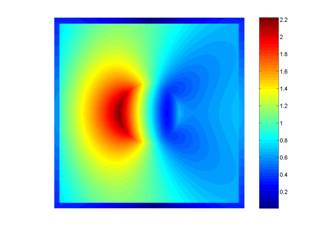
Lens of negative refractive index, was proposed by J. B. Pendry in 2000. Negative refraction index is based upon Snell’s law. The refractive wave propagates forward to the same side relative to the normal as incident wave. In photonic crystals, it seems to the light group velocity propagate to a negative refractive material by Snell’s law, when the ratio between the light frequency and the lattice constant is particular. We investigate the focusing effect in 2D hexagonal photonic crystal(PhC) slabs by finite-difference time-domain method.
Fig.4 Negative refraction makes a slab lens.
(5) CELLULAR LABELING WITH GOLD NANOPARTICLES
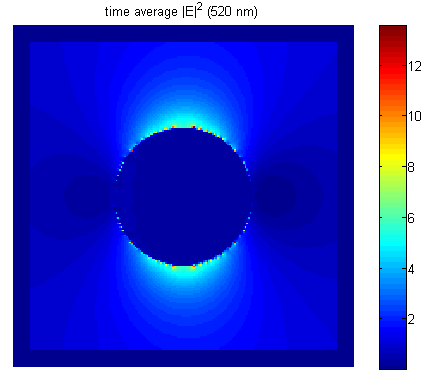
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is a phenomenon of free electrons on the surface of metal coupled to the electromagnetic excitations exhibiting coherent collective oscillations. The SPR of metal nanoparticles have special optical properties that can be applied for biomedical applications; nanoparticles can be conjugated with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (anti-EGFR) antibodies that bind specifically to the cells due to the overexpressed EGFR on the cytoplasmic membrane of the cancerous cells. We build a simple model to describe the nanoparticles’ distribution in cancerous and normal cells. The finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method and the Drude-CP (Drude-critical point) model are employed to simulate the nanoparticles in the biological cells. Metal nanoparticles are in general optically stable, and resistive to photobleaching. In particular, gold nanoparticles are toxic-free, which makes them very suitable for human body. Therefore, metal nanoparticles have potential for labeling of biological cells and other applications.
Fig.5 Time average electrical field intensity of oscillation wavelength 520nm